SQLite Intersect
Summary: in this tutorial, you will learn how to use the SQLite INTERSECT operator.
Introduction to SQLite INTERSECT operator
SQLite INTERSECT operator compares the result sets of two queries and returns distinct rows that are output by both queries.
The following illustrates the syntax of the INTERSECT operator:
SELECT select_list1
FROM table1
INTERSECT
SELECT select_list2
FROM table2
The basic rules for combining the result sets of two queries are as follows:
- First, the number and the order of the columns in all queries must be the same.
- Second, the data types must be comparable.
For the demonstration, we will create two tables t1 and t2 and insert some data into both:
CREATE TABLE t1(
v1 INT
);VALUES(1),(2),(3);
v2 INT
);
INSERT INTO t2(v2)
VALUES(2),(3),(4);
The following statement illustrates how to use the INTERSECT operator to compare result sets of two queries:
SELECT v1
FROM t1
INTERSECT
SELECT v2
FROM t2;
Here is the output:
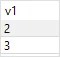
The following picture illustrates the INTERSECT operation:
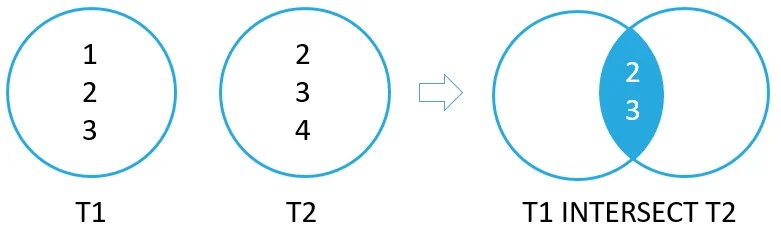
SQLite INTERSECT example
For the demonstration, we will use the customers and invoices tables from the sample database.
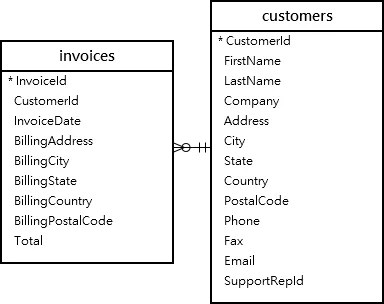
The following statement finds customers who have invoices:
SELECT CustomerId
FROM customers
INTERSECT
SELECT CustomerId
FROM invoices
ORDER BY CustomerId;
The following picture shows the partial output:

In this tutorial, you have learned how to use the SQLite INTERSECT operator to compare two queries and return distinct rows that are output by both queries.