MySQL CROSS JOIN
Summary: in this tutorial, you will learn about the MySQL CROSS JOIN clause and how to use it more effectively.
Introduction to MySQL CROSS JOIN clause
Suppose you join two tables using the CROSS JOIN clause. The result set will include all rows from both tables, where each row is the combination of the row in the first table with the row in the second table. In general, if each table has n and m rows respectively, the result set will have nxm rows.
In other words, the CROSS JOIN clause returns a Cartesian product of rows from the joined tables.
The following illustrates the syntax of the CROSS JOIN clause that joins two tables t1 and t2:
SELECT * FROM t1
CROSS JOIN t2;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)
Note that different from the INNER JOIN, LEFT JOIN , and RIGHT JOIN clauses, the CROSS JOIN clause does not have a join predicate. In other words, it does not have the ON or USING clause.
If you add a WHERE clause, in case table t1 and t2 has a relationship, the CROSS JOIN works like the INNER JOIN clause as shown in the following query:
SELECT * FROM t1
CROSS JOIN t2
WHERE t1.id = t2.id;
Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)
MySQL CROSS JOIN clause examples
Let’s set up some tables to demonstrate the CROSS JOIN clause.
Setting up sample tables
First, create a new database salesdb:
CREATE DATABASE IF NOT EXISTS salesdb;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)
Second, switch the current data to the new database salesdb:
USE salesdb;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)
Third, create new tables in the salesdb database:
CREATE TABLE products (
id INT PRIMARY KEY AUTO_INCREMENT,
product_name VARCHAR(100),
price DECIMAL(13,2 )
);id INT PRIMARY KEY AUTO_INCREMENT,
store_name VARCHAR(100)
);
product_id INT,
store_id INT,
quantity DECIMAL(13 , 2 ) NOT NULL,
sales_date DATE NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (product_id , store_id),
FOREIGN KEY (product_id)
REFERENCES products (id)
ON DELETE CASCADE ON UPDATE CASCADE,
FOREIGN KEY (store_id)
REFERENCES stores (id)
ON DELETE CASCADE ON UPDATE CASCADE
);
Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)
Here are the descriptions of the three tables:
- The table
productscontains the products master data that includes product id, product name, and sales price. - The table
storescontains the stores where the products are sold. - The table
salescontains the products that sold in a particular store by quantity and date.
Finally, insert data into the three tables. Suppose that we have three products iPhone, iPad and Macbook Pro which are sold in two stores North and South.
INSERT INTO products(product_name, price)
VALUES('iPhone', 699),
('iPad',599),
('Macbook Pro',1299);VALUES(‘North’),
(‘South’);
VALUES(1,1,20,‘2017-01-02’),
(1,2,15,‘2017-01-05’),
(1,3,25,‘2017-01-05’),
(2,1,30,‘2017-01-02’),
(2,2,35,‘2017-01-05’);
Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)
MySQL CROSS JOIN example
This statement returns total sales for each store and product, you calculate the sales and group them by store and product as follows:
SELECT
store_name,
product_name,
SUM(quantity * price) AS revenue
FROM
sales
INNER JOIN
products ON products.id = sales.product_id
INNER JOIN
stores ON stores.id = sales.store_id
GROUP BY store_name , product_name;
Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)
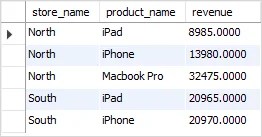
Now, what if you want to know also which store had no sales of a specific product. The query above could not answer this question.
To solve the problem, you need to use the CROSS JOIN clause.
First, use the CROSS JOIN clause to get the combination of all stores and products:
SELECT
store_name, product_name
FROM
stores AS a
CROSS JOIN
products AS b;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)

Next, join the result of the query above with a query that returns the total of sales by store and product. The following query illustrates the idea:
SELECT
b.store_name,
a.product_name,
IFNULL(c.revenue, 0) AS revenue
FROM
products AS a
CROSS JOIN
stores AS b
LEFT JOIN
(SELECT
stores.id AS store_id,
products.id AS product_id,
store_name,
product_name,
ROUND(SUM(quantity * price), 0) AS revenue
FROM
sales
INNER JOIN products ON products.id = sales.product_id
INNER JOIN stores ON stores.id = sales.store_id
GROUP BY stores.id, products.id, store_name , product_name) AS c ON c.store_id = b.id
AND c.product_id= a.id
ORDER BY b.store_name;
Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)
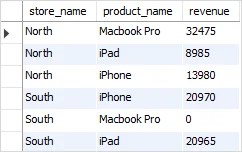
Note that the query used the IFNULL function to return 0 if the revenue is NULL (in case the store had no sales).
By using the CROSS JOIN clause this way, you can answer a wide range of questions e.g., find the sales revenue by salesman, month even if the salesman has no sales in a particular month.