SQLite Python: Inserting Data
Summary: in this tutorial, you will learn how to insert rows into a table in the SQLite database from a Python program using the sqlite3 module.
To insert rows into a table in SQLite database, you use the following steps:
- First, connect to the SQLite database by creating a Connection object.
- Second, create a
Cursorobject by calling the cursor method of theConnectionobject. - Third, execute an INSERT statement. If you want to pass arguments to the
INSERTstatement, you use the question mark (?) as the placeholder for each argument.
SQLite Python – inserting rows example
Let’s insert a new project into the projects table and some tasks into the tasks table that we created in the creating tables from a Python program tutorial.

First, create a new function to establish a database connection to an SQLitte database specified by the database file.
def create_connection(db_file):
""" create a database connection to the SQLite database
specified by db_file
:param db_file: database file
:return: Connection object or None
"""
conn = None
try:
conn = sqlite3.connect(db_file)
except Error as e:
print(e) return conn
Code language: Python (python)
Next, develop a function to insert a new project into the projects table.
def create_project(conn, project):
"""
Create a new project into the projects table
:param conn:
:param project:
:return: project id
"""
sql = ''' INSERT INTO projects(name,begin_date,end_date)
VALUES(?,?,?) '''
cur = conn.cursor()
cur.execute(sql, project)
conn.commit()
return cur.lastrowidCode language: Python (python)
In this function, we used the lastrowid attribute of the Cursor object to get back the generated id.
Then, develop another function for inserting rows into the tasks table.
def create_task(conn, task):
"""
Create a new task
:param conn:
:param task:
:return:
""" sql = ''' INSERT INTO tasks(name,priority,status_id,project_id,begin_date,end_date)
VALUES(?,?,?,?,?,?) '''
cur = conn.cursor()
cur.execute(sql, task)
conn.commit()
return cur.lastrowid
Code language: Python (python)
After that, develop the main() function that creates a new project and two tasks associated with the project.
def main():
database = r"C:\sqlite\db\pythonsqlite.db" # create a database connection
conn = create_connection(database)
with conn:
# create a new project
project = ('Cool App with SQLite & Python', '2015-01-01', '2015-01-30');
project_id = create_project(conn, project)
# tasks
task_1 = ('Analyze the requirements of the app', 1, 1, project_id, '2015-01-01', '2015-01-02')
task_2 = ('Confirm with user about the top requirements', 1, 1, project_id, '2015-01-03', '2015-01-05')
# create tasks
create_task(conn, task_1)
create_task(conn, task_2)
Code language: Python (python)
And call the main() function:
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()Code language: Python (python)
Here is the full program:
import sqlite3
from sqlite3 import Errordef create_connection(db_file):
""" create a database connection to the SQLite database
specified by db_file
:param db_file: database file
:return: Connection object or None
"""
conn = None
try:
conn = sqlite3.connect(db_file)
except Error as e:
print(e)
return conn
def create_project(conn, project):
"""
Create a new project into the projects table
:param conn:
:param project:
:return: project id
"""
sql = ''' INSERT INTO projects(name,begin_date,end_date)
VALUES(?,?,?) '''
cur = conn.cursor()
cur.execute(sql, project)
conn.commit()
return cur.lastrowid
def create_task(conn, task):
"""
Create a new task
:param conn:
:param task:
:return:
"""
sql = ''' INSERT INTO tasks(name,priority,status_id,project_id,begin_date,end_date)
VALUES(?,?,?,?,?,?) '''
cur = conn.cursor()
cur.execute(sql, task)
conn.commit()
return cur.lastrowid
def main():
database = r"C:\sqlite\db\pythonsqlite.db"
# create a database connection
conn = create_connection(database)
with conn:
# create a new project
project = ('Cool App with SQLite & Python', '2015-01-01', '2015-01-30');
project_id = create_project(conn, project)
# tasks
task_1 = ('Analyze the requirements of the app', 1, 1, project_id, '2015-01-01', '2015-01-02')
task_2 = ('Confirm with user about the top requirements', 1, 1, project_id, '2015-01-03', '2015-01-05')
# create tasks
create_task(conn, task_1)
create_task(conn, task_2)
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
Code language: Python (python)
Finally, connect to the database via sqlite3 shell and query data from the projects and tasks tables to check if the data has been inserted successfully.
Use these commands to format the output:
.header on
.mode columnCode language: Shell Session (shell)
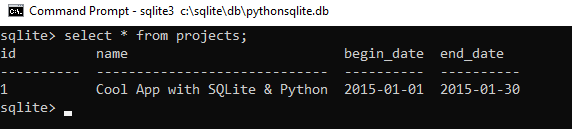
And use this SELECT statement to query data from the projects table:
SELECT * FROM projects;Code language: Shell Session (shell)
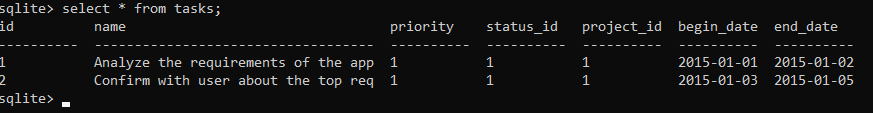
And use the following SELECT statement to query data from the tasks table:
SELECT * FROM tasks;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)
In this tutorial, you have learned how to insert rows into tables in the SQLite database from a Python program.