MySQL Insert
Summary: in this tutorial, you will learn how to use the MySQL INSERT statement to insert one or more rows into a table.
Introduction to the MySQL INSERT statement
The INSERT statement allows you to insert one or more rows into a table. The following illustrates the syntax of the INSERT statement:
INSERT INTO table(c1,c2,...)
VALUES (v1,v2,...);In this syntax,
- First, specify the table name and a list of comma-separated columns inside parentheses after the
INSERT INTOclause. - Then, put a comma-separated list of values of the corresponding columns inside the parentheses following the
VALUESkeyword.
The number of columns and values must be the same. In addition, the positions of columns must be corresponding with the positions of their values.
To insert multiple rows into a table using a single INSERT statement, you use the following syntax:
INSERT INTO table(c1,c2,...)
VALUES
(v11,v12,...),
(v21,v22,...),
...
(vnn,vn2,...);Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)
In this syntax, rows are separated by commas in the VALUES clause.
MySQL INSERT examples
Let’s create a new table named tasks for practicing the INSERT statement.
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS tasks (
task_id INT AUTO_INCREMENT,
title VARCHAR(255) NOT NULL,
start_date DATE,
due_date DATE,
priority TINYINT NOT NULL DEFAULT 3,
description TEXT,
PRIMARY KEY (task_id)
);Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)
1) MySQL INSERT – simple INSERT example
The following statement inserts a new row into the tasks table:
INSERT INTO tasks(title,priority)
VALUES('Learn MySQL INSERT Statement',1);Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)
MySQL returns the following message:
1 row(s) affectedCode language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)
It means that one row has been inserted into the tasks table successfully.
This query returns data from the tasks table:
SELECT * FROM tasks;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)
Here is the output:

In this example, we specified the values for only title and priority columns. For other columns, MySQL uses the default values.
The task_id column is an AUTO_INCREMENT column. It means that MySQL generates a sequential integer whenever a row is inserted into the table.
The start_date, due_date, and description columns use NULL as the default value, therefore, MySQL uses NULL to insert into these columns if you don’t specify their values in the INSERT statement.
2) MySQL INSERT – Inserting rows using default value example
If you want to insert a default value into a column, you have two ways:
- Ignore both the column name and value in the
INSERTstatement. - Specify the column name in the
INSERT INTOclause and use theDEFAULTkeyword in theVALUESclause.
The following example demonstrates the second way:
INSERT INTO tasks(title,priority)
VALUES('Understanding DEFAULT keyword in INSERT statement',DEFAULT);Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)
In this example, we specified the priority column and the DEFAULT keyword.
Because the default value for the column priority is 3 as declared in the table definition:
priority TINYINT NOT NULL DEFAULT 3Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)
MySQL uses the number 3 to insert into the priority column.
The following statement returns the contents of the tasks table after the insert:
SELECT * FROM tasks;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)

3) MySQL INSERT – Inserting dates into the table example
To insert a literal date value into a column, you use the following format:
'YYYY-MM-DD'Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)
In this format:
YYYYrepresents a four-digit year e.g., 2018.MMrepresents a two-digit month e.g., 01, 02, and 12.DDrepresents a two-digit day e.g., 01, 02, 30.
The following statement inserts a new row to the tasks table with the start and due date values:
INSERT INTO tasks(title, start_date, due_date)
VALUES('Insert date into table','2018-01-09','2018-09-15');Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)
The following picture shows the contents of the tasks table after the insert:

It is possible to use expressions in the VALUES clause. For example, the following statement adds a new task using the current date for start date and due date columns:
INSERT INTO tasks(title,start_date,due_date)
VALUES('Use current date for the task',CURRENT_DATE(),CURRENT_DATE())Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)
In this example, we used the CURRENT_DATE() function as the values for the start_date and due_date columns. Note that the CURRENT_DATE() function is a date function that returns the current system date.
Here are the contents of the tasks table after insert:

4) MySQL INSERT – Inserting multiple rows example
The following statement inserts three rows into the tasks table:
INSERT INTO tasks(title, priority)
VALUES
('My first task', 1),
('It is the second task',2),
('This is the third task of the week',3);Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)
In this example, each row data is specified as a list of values in the VALUES clause.
MySQL returns the following message:
3 row(s) affected Records: 3 Duplicates: 0 Warnings: 0Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)
It means that the three rows have been inserted successfully with no duplicates or warnings.
SELECT * FROM tasks;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)
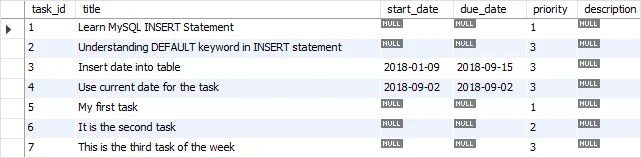
The table tasks has the following data:
In this tutorial, you have learned how to use the MySQL INSERT statement to add one or more rows into a table.